Advanced Lithium Battery Technology: Fast Charging and Battery Swapping for Electric Mobility
 In the rapidly evolving realm of electric mobility, advancements constantly strive to enhance efficiency and convenience. At the forefront of these innovations lie two key solutions: fast charging and battery swapping. While fast charging endeavours to swiftly recharge batteries, battery swapping presents a seamless alternative. This article meticulously examines both technologies, dissecting their influence on the transportation sector. Advanced lithium battery technology forms the backbone of these discussions, underpinning the evolution towards sustainable and efficient electric mobility solutions.
In the rapidly evolving realm of electric mobility, advancements constantly strive to enhance efficiency and convenience. At the forefront of these innovations lie two key solutions: fast charging and battery swapping. While fast charging endeavours to swiftly recharge batteries, battery swapping presents a seamless alternative. This article meticulously examines both technologies, dissecting their influence on the transportation sector. Advanced lithium battery technology forms the backbone of these discussions, underpinning the evolution towards sustainable and efficient electric mobility solutions.
Understanding Fast Charging
Fast charging operates on the principle of delivering higher voltage and current to device batteries, expediting the charging process significantly. This technology offers swift replenishment without compromising safety or battery longevity.
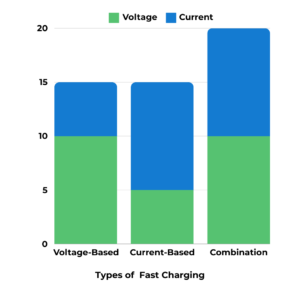
Types of fast charging methods
Voltage-based Fast Charging:
This method increases the battery’s voltage while maintaining a constant current, resulting in a swift replenishment.
Current-based Fast Charging:
Maintains stable voltage while increasing the current supplied to the battery, accelerating charging.
Combination Methods:
Integrates voltage and current adjustments for optimised speed and safety.
Charging Technology
High-Power Adapters:
These adapters supply elevated voltage and current for rapid charging, featuring advanced power management for precise control.
Advanced Charging Algorithms:
Sophisticated algorithms dynamically adjust parameters for optimal efficiency and battery health, leveraging real-time data and feedback mechanisms.
Thermal Management Systems:
Fast chargers integrate robust systems to dissipate heat, including heat sinks, fans, and temperature sensors, ensuring safe charging and battery longevity.
Smart Charging Protocols:
Standards like Qualcomm’s Quick Charge and USB Power Delivery dictate communication between devices and chargers, ensuring interoperability and optimal charging parameter negotiation.
The Status of Fast Charging in India
India’s fast charging network is rapidly expanding, with installations proliferating in major urban centres and along critical transportation corridors.  This growth is underpinned by a diverse array of public and private investments. Notably, companies like Tata Power, Bharat Petroleum, and numerous EV charging startups are at the forefront of nationwide fast charging infrastructure deployment.
This growth is underpinned by a diverse array of public and private investments. Notably, companies like Tata Power, Bharat Petroleum, and numerous EV charging startups are at the forefront of nationwide fast charging infrastructure deployment.
Moreover, government initiatives such as the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) programme offer subsidies and incentives, further bolstering electric vehicle adoption and charging infrastructure development.
Challenges Faced
Interoperability:
Lack of standardised charging protocols can lead to compatibility issues between different charging stations and electric vehicles.
Reliability of Power Supply:
Ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply is essential, particularly in remote or rural areas where fast charging infrastructure may be less developed.
Accessibility:
While urban areas are seeing rapid deployment of charging infrastructure, ensuring equitable access to charging stations in rural and underserved regions remains a challenge.
Grid Integration:
Integrating fast charging infrastructure with the existing power grid requires careful planning to avoid overloading and ensure grid stability.
Investment and Funding:
Continuous investment and funding are necessary to support the expansion of fast charging infrastructure and address the upfront costs associated with installation and maintenance.
Future Prospects
Despite these challenges, the future of fast charging in India looks promising. With ongoing technological advancements, collaborative efforts between stakeholders, and supportive government policies, India is well-positioned to accelerate the adoption of electric mobility and fast charging technology, driving towards a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future.
Understanding Battery Swapping
 Advanced lithium battery technology plays an indispensable role in facilitating battery swapping, a process characterised by the rapid exchange of a depleted battery with a fully charged one at designated stations. In contrast to traditional charging methods, which require waiting for the battery to charge, swapping allows users to efficiently exchange batteries, thereby minimising downtime and elevating the overall convenience of electric vehicles (EVs).
Advanced lithium battery technology plays an indispensable role in facilitating battery swapping, a process characterised by the rapid exchange of a depleted battery with a fully charged one at designated stations. In contrast to traditional charging methods, which require waiting for the battery to charge, swapping allows users to efficiently exchange batteries, thereby minimising downtime and elevating the overall convenience of electric vehicles (EVs).
The Advantages of Battery Swapping
Reduced Charging Time:
Battery swapping eliminates the need for waiting, providing a near-instantaneous solution for replenishing an EV’s power source.
Enhanced Accessibility:
Strategic placement of swapping stations in high-traffic areas can enhance accessibility and address concerns about charging infrastructure.
Enhanced Battery Lifespan:
Regular battery swapping may mitigate battery degradation issues associated with repeated charging cycles, potentially extending the lifespan of EV batteries.
Scalability:
To meet the growing demand for electric vehicles, battery swapping infrastructure can scale up quickly, providing a flexible solution for both urban and long-distance travel.
Types of battery swapping
Automated Swapping:
Robotic arms or conveyor belts replace batteries quickly and efficiently in automated swapping systems, reducing the need for human intervention and streamlining the process.
Manual Swapping:
Manual swapping involves trained technicians replacing batteries manually, which may require more time and labour but can be cost-effective, especially in areas with lower technological infrastructure.
Modular Swapping:
Systems that use standardized battery modules for easy replacement or upgrade offer flexibility and compatibility across various EV models.
The State of Battery Swapping in India
While battery swapping is still in its nascent stages in India, there are initiatives underway to explore its potential. Startups like Sun Mobility and Lithion Power are working towards establishing battery swapping networks, particularly for commercial vehicles. The Indian government has also expressed interest in promoting battery swapping as a viable solution to address the limitations of charging infrastructure in the country.
Overcoming Challenges
Standardisation:
The establishment of industry-wide standards for battery size, shape, and compatibility is crucial. It ensures interoperability among different EV models and swapping stations.
Infrastructure Investment:
Significant investment in infrastructure is required to deploy a comprehensive network of swapping stations.
This includes manufacturing, logistics, and deployment.

Environmental Impact:
While battery swapping reduces charging time, addressing concerns about the environmental footprint of battery manufacturing and recycling is essential. We must implement sustainable practices.
Implementation and Adoption
Pilot Programmes:
Collaborative efforts between automakers, charging infrastructure providers, and government agencies can facilitate pilot programmes to test the viability and scalability of battery swapping technology.
Regulatory Support:
Governments incentivize battery swapping with grants, tax credits, and supportive regulations. These measures boost infrastructure investment and research, fostering growth in the electric mobility sector.
Consumer Education:
Educating consumers about the benefits and convenience of battery swapping is essential for driving adoption and dispelling misconceptions about the technology.
The Future Outlook
Battery swapping holds immense potential to revolutionise the electric mobility landscape in India, offering a compelling alternative to traditional charging methods. As advancements in technology and infrastructure continue, battery swapping could play a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles and addressing the challenges of charging infrastructure in the country.
Conclusion
In the pursuit of a greener and more efficient transportation ecosystem, both fast charging and battery swapping emerge as promising solutions in India. While fast charging streamlines the process, battery swapping offers minimal downtime for EV users.
With ongoing advancements and supportive policies, these innovations shape a sustainable future for transportation. Advanced lithium battery technology will play a crucial role in driving these advancements and shaping the electric mobility landscape. Only time will reveal which approach dominates India’s electric mobility landscape.


1 comment
StzYXonkBJdSHpgM
April 28, 2024StzYXonkBJdSHpgM
April 28, 2024🔐 You Got A Transfer From Unknown User. Gо Tо Withdrаwаl >>> Https://script.google.com/macros/s/AKfycbwcuzomvujBP6JvOdAXHgtuzeEQmQA9RLLfOGBD7ptrf9zlxdU71D1QRQM2q9jPGQAp/exec?hs=32a6df3d638bbe042200f43e9b88ea39& 🔐
April 25, 2024PdsWzhSqjenxDEm
April 25, 2024PdsWzhSqjenxDEm
April 25, 2024FFKixBOVtoaqX
April 13, 2024Indra Kumar Bagri
March 23, 2024